Understanding Critical Values in Statistics: Explanation and Calculations
Critical values play a key role in hypothesis testing. They act as thresholds that help us make decisions about the null hypothesis.Reject the null hypothesis if the test statistic (a value calculated from the data) falls in the critical region (beyond the critical value). If the test statistic lies in the non-critical region (below the critical value), we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
The critical value is computed by the selected significance
level. Commonly used significance levels include 0.05 and 0.01, but they can change
depending on the specific research context.
We will dive deep into the concept of critical value in this
article. We will learn how to determine critical value and gain a better
understanding through examples.
What is Critical Value?
The critical value is a specific numeric threshold that helps us determine whether to reject or not to reject the null hypothesis based on the calculated test statistic.It is determined by the significance level and test statistic distribution.We compare the calculated test statistic to the critical value to make a conclusion about the null hypothesis.
The standard decision-making procedure is as follows:
- The null hypothesis (H0) is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis(H1) when the test statistic is higher than the critical value.
- Never reject the null hypothesis if the test statistic is less than or equal to the critical value.
How to Calculate Critical Value?
To calculate critical value, follow the steps below:
- Start
by determining the significance level (α) for your statistical test. The alpha
level can be calculated by the following formula:
Alpha = 1 – (confidence level /
100)
- Determine
whether a test is a one or two-tailed test.
|
Test Type |
Significance Level (α) Allocation |
Explanation |
|
One-Tailed |
α is used entirely in one direction |
All of α is allocated to either the left or right tail. |
|
Two-Tailed |
α is divided by 2, allocating α/2 to each direction. |
α is evenly split between both the left and right tails. |
- Compute the degree of freedom value. The degrees of freedom are related to the specific test and the sample size. It can be found as:
df = sample size –
1
- Each
test has its unique critical value.A critical value can be determined from a
distribution table using an alpha value corresponding to the type of test
conducted.
- After obtaining the critical value, compare it with the calculated test statistic.
T-Critical Value
The t-critical value is a method that helps us to make statistically sound conclusions about the difference between a sample mean and a population mean. It is used whenthe population standard deviation is unknown and the sample size is less than 30.
How to Find T-Critical Value?
Step 1: Start by
determining the significance level (α).
Step 2:Find the value for
degrees of freedom.
Step 3: Refer to a
t-distribution table.
Step 4: Locate the degrees of freedom (df) in the left column and the significance level (alpha) in the top row of the table. The point where this row and column intersect provides the t-critical value.
Formula to calculate test statistic for a one-sample t-test:
t = (x̄ - μ) / (s / √n)
Where:
- x̄ (x-bar)symbolizes the sample mean.
- μ (mu) stands for the population mean.
- s This represents the sample standard deviation.
- nis the sample size.
Two-sample t-Statistics test:
t = (x̄1 - x̄2) - (μ1 - μ2) / √ ((s1² / n1) + (s2² / n2))
Decision Criteria:
Decisions regarding the null hypothesis are determined by
considering both the computed test statistic and the critical value derived
from the t-distribution.
|
Type of Hypothesis Test |
Rejection Criteria |
|
Right-Tailed Test |
Rejected if t-critical value < test statistic |
|
Left-Tailed Test |
Rejected if t-critical value > test statistic |
|
Two-Tailed Test |
Reject if the test statistic lies in the non-rejection rejoin |
These criteria are commonly used in hypothesis testing to
make decisions about whether to reject the null hypothesis based on the
calculated test statistic and the critical values associated with the chosen
significance level.
Solved Example of Critical Value
Critical values are specific values used in statistical hypothesis testing to determine whether to reject a null hypothesis. Here are some examples of critical values in various statistical tests:
Example:
Given a sample mean of 83, a sample standard deviation of 12.5, and a sample size of 11 test the hypothesis that the value of the population mean is 70 against the alternative that is more than 70 using a 0.05 level of significance.
Solution:
Given:
x̄ = 83, n = 11, s = 12.5, μ = 70, α = 0.05
Step 1:Define the Null and Alternative Hypotheses:
H0: μ = 70
H1: μ> 70
Step 2:Choose the Significance Level:
In this example, the significance level (alpha) is 0.05.
Step 3:Calculate the Test Statistic:
The test statistic for a one-sample t-test can be computed using the formula:
T-statistic test = (x̄ - μ) / (s / √n)
= (83 – 70) / (12.5/√11)
= 13/3.76
= 3.457
Step 4:Find the Critical Value:
α = 0.05
Degree of freedom = sample size – 1
df = 11 – 1 = 10
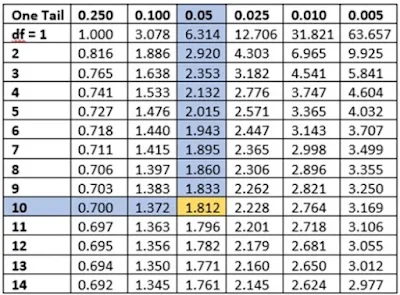
Take the t-distribution table and find the degrees of freedom (10) in the left column and the significance level (0.05) in the top row of the table.
Take the point where this row and column intersect.This value will be our t-critical value.
Thus, 1.812 is the t-critical value.
Step 5:Make a Decision:
Compare the calculated test statistic (3.43) to the critical t-value (1.812).
Test statistics > t-critical value
Step 6:Draw a Conclusion:
Since the calculated value of t falls in the critical region, reject the null hypothesis (H0).
Summary
In this article, we have explored the concept of critical
value in hypothesis testing. Critical values serve as important thresholds to
make decisions regarding the null hypothesis. They are determined by the chosen
significance level and the distribution of the test statistic.
The decision-making process involves comparing the calculated test statistic to the critical value. This article will help you to draw statistically sound conclusions in various statistical tests.





No comments:
Post a Comment